In the last years, IoT (Internet of Things) networks have taken a strong position in the international market. The software and equipment which is used in the deployment and service of wireless networks has already accumulated a wide assortment and allows you to solve any task.
When a project is starting, it is not obvious which communication standard should be chosen, especially since now there are a huge number of them. Let us consider three popular technologies that now are dividing the market in the field of the Internet of Things.
LoRaWAN, NB-IoT or GSM?
Often the selection criterion is the set of necessary functions of the equipment. That is, a specific set of interfaces is primary, and then you must work with the technology that the device supports. But what if the required hardware is available in all variants or supports more than one technology?
In this case, it is worth taking a closer look at the communication standards, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The first question to be solved:
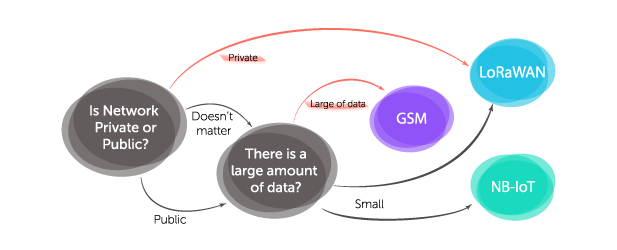
Is there a necessary for private network or can you use the services of a global operator? In many cities it is already possible to find a LoRaWAN network operator, and NB-IoT networks are supported by many cellular operators. It all depends on which networks the data collection area is already covered with. If there is no LoRaWAN operator, then you can deploy the private network, which cannot be said about GSM - it either exists or not. Sometimes a cellular operator can connect to NB-IoT an area already covered by a GSM network, but under certain conditions.
Need private network?
It is much easier and cheaper to deploy LoRaWAN from scratch than NB-IoT or GSM. So, if it is necessary to fully control the process of collecting and transmitting information, the choice is LoRaWAN definitely.
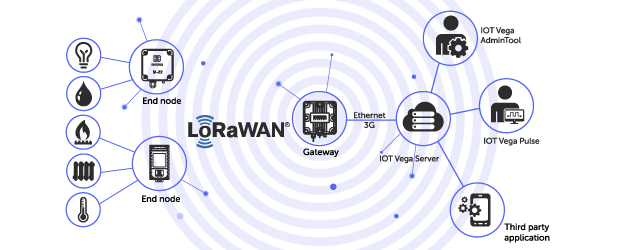
Let us assume you do not need the private network
And there are all operators with great deals, ready to provide support and service. What else should you pay attention to?
Amount of transferred data
Despite the fact that in the field of IoT the transfer of large amounts of data is not usually required there are some exceptions. One of the strong examples is the collection of data from electricity meters. LoRaWAN and NB-IoT technologies have limitations on the number of parameters collected from electricity meters and you must choose the most necessary ones. To download the entire array of information provided by the manufacturer of electricity meters, including archives of readings for several months, GSM is simply irreplaceable.
Perhaps, for your project, the amount of transferred data will become the main criterion for choosing a technology.
What is next?
And then there are technical subtleties, the differences in which are difficult to detect with the naked eye.
Small differences in bandwidth, data transfer rate, method of communication - in general, lead us to the conclusion that LoRaWAN technology has a slightly lower power consumption and a slightly cheaper maintenance, while NB-IoT and GSM technologies are slightly more reliable and better suited for systems requiring an emergency response.
If telematic data collection is required from a large or open area, then the LoRaWAN network offers an ideal price-performance ratio.
In the case when it is necessary to quickly send a command for control in response to the received data, or receiving data is critical, then preference should be given to NB-IoT and GSM modems.
 Vega BS-1
Vega BS-1 Vega BS-2
Vega BS-2 Vega BS-1.2
Vega BS-1.2 Vega BS-2.2
Vega BS-2.2 Vega BS-0.1
Vega BS-0.1 Vega BS-3
Vega BS-3 Antenna 868-01
Antenna 868-01 Antenna 868-01-A10
Antenna 868-01-A10 Vega SI-11
Vega SI-11 Vega SI-12
Vega SI-12 Vega SI-13-232
Vega SI-13-232 Vega SI-13-485
Vega SI-13-485 Vega SI-21
Vega SI-21 Vega SI-23-232
Vega SI-23-232 Vega SI-23-485
Vega SI-23-485 Vega SI-22
Vega SI-22 Vega NB-11
Vega NB-11 Vega NB-12
Vega NB-12 Vega NB-13
Vega NB-13 Vega NB-14
Vega NB-14 Vega NB-15
Vega NB-15 Betar-Vega SHVE/SGVE
Betar-Vega SHVE/SGVE Vega TL-11
Vega TL-11 Vega M-BUS-1
Vega M-BUS-1 Vega M-BUS-2
Vega M-BUS-2 Vega TP-11
Vega TP-11 Vega TD-11
Vega TD-11 Vega GM-2
Vega GM-2 Vega SH-2
Vega SH-2 Vega LM-1
Vega LM-1 Vega LM-210
Vega LM-210 Betar-Vega SHVE/SGVE
Betar-Vega SHVE/SGVE CE2726A R01
CE2726A R01 CE2726A W03
CE2726A W03 CE2727A R02
CE2727A R02 CE2727A B04
CE2727A B04 Mercury 206
Mercury 206 Betar-Vega SGBM-1.6
Betar-Vega SGBM-1.6 Vega TS-11
Vega TS-11 Vega Smart-UM0101
Vega Smart-UM0101 Vega Smart-HS0101
Vega Smart-HS0101 Vega Smart-MC0101
Vega Smart-MC0101 Vega Smart-WB0101
Vega Smart-WB0101 Vega Smart Badge
Vega Smart Badge Vega TD-21
Vega TD-21 Vega Smart-AS0101
Vega Smart-AS0101 Vega Smart-MS0101
Vega Smart-MS0101 Vega Smart-SS0101
Vega Smart-SS0101 Vega DP-1
Vega DP-1 Vega USB-UART
Vega USB-UART Vega FSK Dongle
Vega FSK Dongle Vega RF32WL
Vega RF32WL Vega RM868-UFL
Vega RM868-UFL Vega RM868-CPA
Vega RM868-CPA VEKTOR-101
VEKTOR-101 Vega Smart Tab
Vega Smart Tab Vega BP 3.6V
Vega BP 3.6V Vega Smart Tab-S
Vega Smart Tab-S Vega BS-4
Vega BS-4 Vega BS-4 PRO
Vega BS-4 PRO

